Public vs. Private Capital Markets
Throughout most of the 20th century, public capital markets have provided the fuel for tremendous economic growth, job creation, innovation and personal wealth-building. Access to a large, liquid pool of capital has enabled companies to finance their growth in a cost-effective manner, thus enabling management teams to invest in new products and technologies, create millions of jobs, and attain a company’s full potential.
The lure of an initial public offering, and the potential for future gains, has attracted employees to start-up ventures that otherwise might be starved for talent. And investing in publicly traded assets has been an exceptional source of wealth-accumulation for individuals and families, notably through their pension funds.
More recently, corporations and investors have been bypassing public markets in favour of raising funds via private equity, late-stage venture capital or direct lending. Consider that the number of domestic companies listed on US exchanges, which from a peak of some 7,500 in 1996 has since declined by nearly 40%, as shown below – precipitous, despite there being some signs of recently renewed growth.
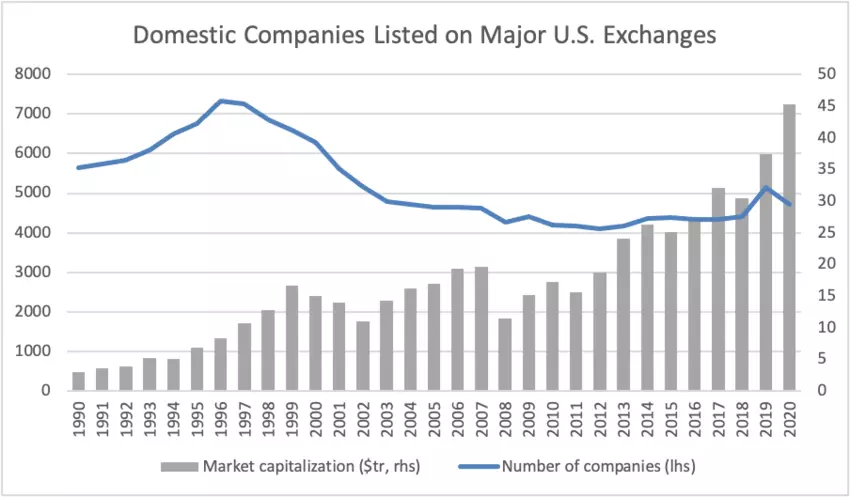
The clear increase in market capitalization in recent years is driven by a relatively small subset of big firms in the technology space, further increasing concerns of concentration. Relatedly, private market assets under management globally (including private equity, venture capital, real estate, private debt and infrastructure) rose to $6.5 trillion in 2019, the highest level on record.
Growth Capital and Access to Investment Choices
As a number of corporate leaders and academic experts have pointed out, if companies continue to raise money through private mechanisms, there are consequences for the democratization of capitalism and wealth creation.
There are, to be sure, strong arguments in favour of private capital. It enables companies to finance their growth without the pressures of quarter-to-quarter “short termism” that can plague publicly traded companies. It also has been suggested that “agency costs” may be reduced for private companies, as the interests of managements and investors are closely aligned. However, a further contraction of public markets would entail some risks:
Limiting choices of retail investors: By definition, private markets are not available to the general public. Thus, the average retail investor is denied access to potentially attractive investments in some of the world’s fastest growing enterprises. This places a particularly heavy burden on those who invest on their own or through defined-contribution retirement plans, and typically cannot access private investments that might otherwise be available to build retirement assets.
Loss of transparency: The regulatory disclosure requirements imposed on public companies, as well as the scrutiny of outside investors, provides a fairly high level of transparency as to business strategies, operational and financial performance, corporate governance, and risk exposure. Operating in the public eye, while admittedly onerous, does provide managements and boards with an extra measure of discipline.
Reduced access to liquid capital: Public markets have long been a major source of capital to fund growing enterprises or to enable businesses to fortify their balance sheets in difficult times. Allowing the public markets to contract significantly would remove an important source of capital, which could become a serious problem should private markets “dry up” in a downturn.
A New Approach to Private Capital
The purpose of this post is not to suggest that public markets are inherently better than private markets, but rather that there are advantages to both types of capital. There are a number of possible solutions that can be explored to ensure that the benefits of public markets – such as investor access and transparency – are not completely lost for private markets.
1. Democratize Private Markets. Since there currently is no viable way for most retail investors to participate in private financings, large public institutional investors could provide a near-term solution by issuing securities backed by private market assets in their portfolios.
Such private asset-backed securities might have limited liquidity i.e. sellable only at the end of a quarter. For institutional investors, we already observe a strong increase in secondary markets for private equity which could form a first step towards making those instruments more liquid.
The US guidance for the inclusion of illiquid investments, such as private equity, into retail pension plans is another encouraging development. A longer-term solution could be to develop exchange-traded funds (ETFs) tied to private market debt or equity.
Finally, the recent increase in SPAC issuance creates a bridge between public and private markets, in theory combining the depth of public markets with the specialist ownership usually seen in private markets – while it remains to be seen whether volumes are sustainable, it is certainly an interesting development. As with all forms of innovation, pragmatic and sensible regulation to protect the interests of retail investors will be a necessary support mechanism.
2. Foster public company-like discipline. Investors should play active roles in fostering good governance policies and practices on the part of the private companies in their portfolios. This is already being pursued by many private market investors, who realize that good governance is a clear avenue for value creation. Also, long-term investment and engagement might be increased through a system in which voting rights per share were linked to the share-holding period.
3. Instil a sustainability mindset. Environmental, social and corporate governance (ESG) issues have become more important to investors in public companies. Asset owners should adopt a similar focus on ESG, and consider including sustainability metrics in their evaluation and selection of private market general partners.
About Capital Engine®
Capital Engine® facilitates the creation of efficient and trusted online private capital and alternative investment marketplaces, through our tiered business ecosystem: private label platforms, strategic partnerships and inhouse marketplace for private placements.
Capital Engine® provides a comprehensive, integrated suite of digital investment tools, back office technology and distribution platform to connect private capital with HNW individuals and family office capital.
Our software helps leverage the opportunity to better originate and showcase a diverse selection of private investment deals and offer these to investors i.e. a deal’s potential viability can be better assessed, market appetite determined and transaction promptly closed.
Looking to Raising Capital
The lure of an initial public offering, and the potential for future gains, has attracted employees to start-up ventures that otherwise might be starved for talent. And investing in publicly traded assets has been an exceptional source of wealth-accumulation for individuals and families, notably through their pension funds.
More recently, corporations and investors have been bypassing public markets in favour of raising funds via private equity, late-stage venture capital or direct lending. Consider that the number of domestic companies listed on US exchanges, which from a peak of some 7,500 in 1996 has since declined by nearly 40%, as shown below – precipitous, despite there being some signs of recently renewed growth.

The clear increase in market capitalization in recent years is driven by a relatively small subset of big firms in the technology space, further increasing concerns of concentration. Relatedly, private market assets under management globally (including private equity, venture capital, real estate, private debt and infrastructure) rose to $6.5 trillion in 2019, the highest level on record.
Growth Capital and Access to Investment Choices
As a number of corporate leaders and academic experts have pointed out, if companies continue to raise money through private mechanisms, there are consequences for the democratization of capitalism and wealth creation.
There are, to be sure, strong arguments in favour of private capital. It enables companies to finance their growth without the pressures of quarter-to-quarter “short termism” that can plague publicly traded companies. It also has been suggested that “agency costs” may be reduced for private companies, as the interests of managements and investors are closely aligned. However, a further contraction of public markets would entail some risks:
Limiting choices of retail investors: By definition, private markets are not available to the general public. Thus, the average retail investor is denied access to potentially attractive investments in some of the world’s fastest growing enterprises. This places a particularly heavy burden on those who invest on their own or through defined-contribution retirement plans, and typically cannot access private investments that might otherwise be available to build retirement assets.
Loss of transparency: The regulatory disclosure requirements imposed on public companies, as well as the scrutiny of outside investors, provides a fairly high level of transparency as to business strategies, operational and financial performance, corporate governance, and risk exposure. Operating in the public eye, while admittedly onerous, does provide managements and boards with an extra measure of discipline.
Reduced access to liquid capital: Public markets have long been a major source of capital to fund growing enterprises or to enable businesses to fortify their balance sheets in difficult times. Allowing the public markets to contract significantly would remove an important source of capital, which could become a serious problem should private markets “dry up” in a downturn.
A New Approach to Private Capital
The purpose of this post is not to suggest that public markets are inherently better than private markets, but rather that there are advantages to both types of capital. There are a number of possible solutions that can be explored to ensure that the benefits of public markets – such as investor access and transparency – are not completely lost for private markets.
1. Democratize Private Markets. Since there currently is no viable way for most retail investors to participate in private financings, large public institutional investors could provide a near-term solution by issuing securities backed by private market assets in their portfolios.
Such private asset-backed securities might have limited liquidity i.e. sellable only at the end of a quarter. For institutional investors, we already observe a strong increase in secondary markets for private equity which could form a first step towards making those instruments more liquid.
The US guidance for the inclusion of illiquid investments, such as private equity, into retail pension plans is another encouraging development. A longer-term solution could be to develop exchange-traded funds (ETFs) tied to private market debt or equity.
Finally, the recent increase in SPAC issuance creates a bridge between public and private markets, in theory combining the depth of public markets with the specialist ownership usually seen in private markets – while it remains to be seen whether volumes are sustainable, it is certainly an interesting development. As with all forms of innovation, pragmatic and sensible regulation to protect the interests of retail investors will be a necessary support mechanism.
2. Foster public company-like discipline. Investors should play active roles in fostering good governance policies and practices on the part of the private companies in their portfolios. This is already being pursued by many private market investors, who realize that good governance is a clear avenue for value creation. Also, long-term investment and engagement might be increased through a system in which voting rights per share were linked to the share-holding period.
3. Instil a sustainability mindset. Environmental, social and corporate governance (ESG) issues have become more important to investors in public companies. Asset owners should adopt a similar focus on ESG, and consider including sustainability metrics in their evaluation and selection of private market general partners.
About Capital Engine®
Capital Engine® facilitates the creation of efficient and trusted online private capital and alternative investment marketplaces, through our tiered business ecosystem: private label platforms, strategic partnerships and inhouse marketplace for private placements.
Capital Engine® provides a comprehensive, integrated suite of digital investment tools, back office technology and distribution platform to connect private capital with HNW individuals and family office capital.
Our software helps leverage the opportunity to better originate and showcase a diverse selection of private investment deals and offer these to investors i.e. a deal’s potential viability can be better assessed, market appetite determined and transaction promptly closed.
Looking to Raising Capital
Latest Articles





